Tdk s conductive epoxy series is a conductive glue mounted device rather than solder mounted.
Cte ceramic capacitor.
Opinions from customers will be used to improve the faqs.
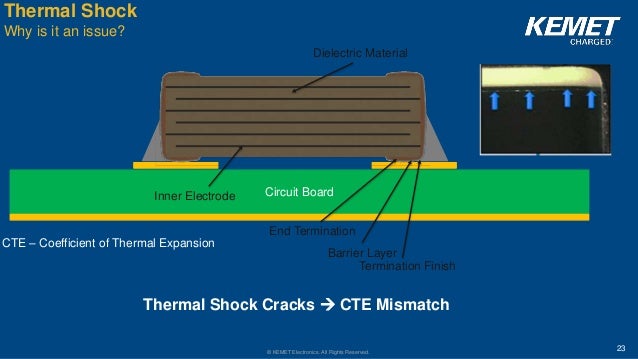
In high temperature environments the connectivity reliability is focused on the solder fillet because there are thermal expansion coefficient differences between the substrate mlcc and solder fillet.
The cte for ceramic capacitors made with barium titanate2 such as class ii x7r mlcc is around 10 ppm c.
The micro crack will propagate along isothermal lines where the capacitor structure received maximum stress.
The termination and ceramic interface during the fastest temperature increases of soldering.
Thermal shock is a complex issue that has been covered earlier in detail1 2 so only an overview of those cracks is presented.
They are also one of the smallest discrete components on the pcb used over overwhelmingly in decoupling application.
A concise guide to ceramic capacitor types march 30 2018 by robert keim this technical brief attempts to dispel some of the fog that surrounds the three character cryptograms used to describe ceramic caps.
Ceramic capacitors configurations material faq.
A ceramic capacitor is a fixed value capacitor where the ceramic material acts as the dielectric it is constructed of two or more alternating layers of ceramic and a metal layer acting as the electrodes the composition of the ceramic material defines the electrical behavior and therefore applications.
We would like to hear your opinions and requests regarding these faqs.
Mlcc stands for multilayer ceramic capacitors.
Ceramic capacitors are vulnerable to cracking because of pcb flexing.
Technical article x7r x5r c0g.
Around 20 ppm c and ceramic with a cte of 10 12 ppm c.
They also have a coefficient of thermal expansion cte difference from the pcb of almost 2.
This propagation takes a long time and is dependent on the physical size of the capacitor cte difference between the substrate and capacitor.
Multilayer ceramic capacitors are sensitive to thermal.
The differences in cte between the mlcc and fr4 have to be compensated for by elasticity that is.
Cte and t are a function of the materials used in the component s manufacture and the rate of change of temperature is dependent on the soldering process.
This tendency is made worse by ag pd being a much better conductor of heat 400 w m k than ceramic 4 5 w m k so that a thermal gradient will exist across the ceramic layer.